Managing DNS
Customizing DNS Zone Configuration
For each new domain name, your Plesk Web Hosting Control Panel automatically creates DNS zone in accordance with the configuration preset defined by Webnames. The domain names should work fine with the automatic configuration, however if you need to perform custom modifications in the domain name zone, you can do that through your control panel.
To view the resource records in a DNS zone of a domain
To see the records currently present in a domain’s DNS zone, go to Websites & Domains > the domain name in question >Hosting & DNS > DNS. You can also add, modify, and remove records on this screen.
Adding Resource Records
To add a record, click Add Record. Select a resource record type, and specify the appropriate data:
- For an A record
 The A-record is used to translate human friendly domain names such as "www.example.com" into IP-addresses such as 23.211.43.53 (machine friendly numbers). you will need to enter the domain name for which you wish to create an A record. If you are simply defining an A record for your main domain, then you should leave the available field empty. If you are defining an A record for a name server
The A-record is used to translate human friendly domain names such as "www.example.com" into IP-addresses such as 23.211.43.53 (machine friendly numbers). you will need to enter the domain name for which you wish to create an A record. If you are simply defining an A record for your main domain, then you should leave the available field empty. If you are defining an A record for a name server In computing, a name server is a computer server that hosts a network service for providing responses to queries against a directory service. It maps a human-recognizable identifier to a system-internal, often numeric, identification or addressing component. This service is performed by the server according to a network service protocol. then you will need to input the appropriate entry for the given name server (ie. ns1). Then, you need to enter the appropriate IP address
In computing, a name server is a computer server that hosts a network service for providing responses to queries against a directory service. It maps a human-recognizable identifier to a system-internal, often numeric, identification or addressing component. This service is performed by the server according to a network service protocol. then you will need to input the appropriate entry for the given name server (ie. ns1). Then, you need to enter the appropriate IP address An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing to which to associate the domain name.
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing to which to associate the domain name. - For an NS record
 NS Resource Records are records in the DNS database to determine which authorative name servers are used for the domain., you will need to enter the domain name for which you wish to create the NS record. If you are defining an NS record for your main domain, then you will leave the available field blank. Then enter the appropriate name server name in the field provided. You will need to enter the complete name (i.e. ns1.mynameserver.com).
NS Resource Records are records in the DNS database to determine which authorative name servers are used for the domain., you will need to enter the domain name for which you wish to create the NS record. If you are defining an NS record for your main domain, then you will leave the available field blank. Then enter the appropriate name server name in the field provided. You will need to enter the complete name (i.e. ns1.mynameserver.com). - For an MX record
 MX-records are used to specify the e-mail server(s) responsible for a domain name.
Each MX-record points to the name of an e-mail server and holds a preference number for that server., you will need to enter the domain for which you are creating the MX record. For the main domain, you would simply leave the available field blank. You will then need to enter your mail exchanger, this is the name of the mail server. If you are running a remote mail server named 'mail.myhostname.com' then you would simply enter 'mail.myhostname.com' into the field provided. You will then need to set the priority for the mail exchanger. Select the priority using the drop-down box: 0 is the highest and 50 is the lowest. Keep in mind you would also need to add the appropriate A record, and/or CNAME if applicable for the remote mail exchange server.
MX-records are used to specify the e-mail server(s) responsible for a domain name.
Each MX-record points to the name of an e-mail server and holds a preference number for that server., you will need to enter the domain for which you are creating the MX record. For the main domain, you would simply leave the available field blank. You will then need to enter your mail exchanger, this is the name of the mail server. If you are running a remote mail server named 'mail.myhostname.com' then you would simply enter 'mail.myhostname.com' into the field provided. You will then need to set the priority for the mail exchanger. Select the priority using the drop-down box: 0 is the highest and 50 is the lowest. Keep in mind you would also need to add the appropriate A record, and/or CNAME if applicable for the remote mail exchange server. - For a CNAME record
 CNAME-records are domain name aliases.
To mask this, CNAME-records can be used to give a single computer multiple names (aliases)., you will need to first enter the alias domain name for which you wish to create the CNAME record. You then need to enter the domain name within which you want the alias to reside. Any domain name can be entered. It does not need to reside on the same server.
CNAME-records are domain name aliases.
To mask this, CNAME-records can be used to give a single computer multiple names (aliases)., you will need to first enter the alias domain name for which you wish to create the CNAME record. You then need to enter the domain name within which you want the alias to reside. Any domain name can be entered. It does not need to reside on the same server. - For a PTR record
 A PTR (Pointer) record is a type of DNS record used for reverse DNS lookups. It maps an IP address to a domain name, essentially the opposite of an A record, which maps a domain name to an IP address. you will first enter the IP address/mask for which you wish to define the pointer. Then enter the appropriate domain name for this IP to be translated to.
A PTR (Pointer) record is a type of DNS record used for reverse DNS lookups. It maps an IP address to a domain name, essentially the opposite of an A record, which maps a domain name to an IP address. you will first enter the IP address/mask for which you wish to define the pointer. Then enter the appropriate domain name for this IP to be translated to. - For a TXT record
 TXT-records are used to hold descriptive text.
They are often used to hold general information about a domain name such as who is hosting it, contact person, phone numbers, etc.
One common use of TXT-records is for SPF (see http://www.openspf.org).
This is however gradually being replaced by the new SPF-record type., you will be able to enter an arbitrary text string, which could be a description or an SPF record
TXT-records are used to hold descriptive text.
They are often used to hold general information about a domain name such as who is hosting it, contact person, phone numbers, etc.
One common use of TXT-records is for SPF (see http://www.openspf.org).
This is however gradually being replaced by the new SPF-record type., you will be able to enter an arbitrary text string, which could be a description or an SPF record TXT-records are used to hold descriptive text.
One common use of TXT-records is for SPF (see http://www.openspf.org)..
TXT-records are used to hold descriptive text.
One common use of TXT-records is for SPF (see http://www.openspf.org).. - For a SRV record
 A Service record (SRV record) is a specification of data in the Domain Name System defining the location, i.e. the hostname and port number, of servers for specified services. It is defined in RFC 2782, and its type code is 33. Some Internet protocols such as the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) often require SRV support by network elements., you will need to enter the service name, protocol name, port number, and target host. You can also specify the priority of service and weight of service in the appropriate fields.
A Service record (SRV record) is a specification of data in the Domain Name System defining the location, i.e. the hostname and port number, of servers for specified services. It is defined in RFC 2782, and its type code is 33. Some Internet protocols such as the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) often require SRV support by network elements., you will need to enter the service name, protocol name, port number, and target host. You can also specify the priority of service and weight of service in the appropriate fields.
To modify a record, click its name. To remove a record, select the checkbox next to the record’s name and click Remove. Note that removing certain records will affect the functioning of your domain. For example, removing the A record will prevent it from resolving. If you made changes to the DNS zone that affect the functioning of your website, you can restore the default DNS records by clicking Reset to Default. This will undo all the changes made to the DNS zone and recreate it according to the server-wide DNS template. Note that any custom records you may have added to the zone will be lost.
The DNS zone also includes the SOA records template. You can see and change the
SOA record![]() Specifies authoritative information about a DNS zone, including the primary name server, the email of the domain administrator, the domain serial number, and several timers relating to refreshing the zone. values in Websites & Domains > DNS Settings >
SOA. Selecting the Use serial number format recommended by IETF
and RIPE checkbox changes the way Plesk stores SOA serial numbers from
the Unix timestamp to the YYYYMMDDNN format recommended by RIPE. Using
the YYYYMMDDNN format is required for many domain registrars, mostly
European ones. If your registrar refuses your SOA serial number,
enabling this option may help.
Specifies authoritative information about a DNS zone, including the primary name server, the email of the domain administrator, the domain serial number, and several timers relating to refreshing the zone. values in Websites & Domains > DNS Settings >
SOA. Selecting the Use serial number format recommended by IETF
and RIPE checkbox changes the way Plesk stores SOA serial numbers from
the Unix timestamp to the YYYYMMDDNN format recommended by RIPE. Using
the YYYYMMDDNN format is required for many domain registrars, mostly
European ones. If your registrar refuses your SOA serial number,
enabling this option may help.
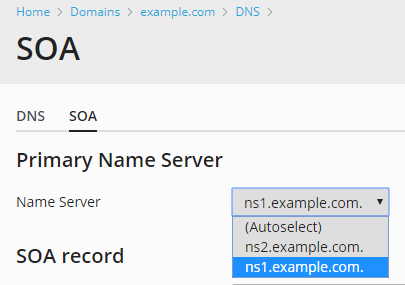
You can explicitly specify which name sever will be the trusted source of data for slave name servers by appointing this name server as the primary one for your domain. To do so, under “Primary Name Server”, select the desired name server.
| NOTE: If SOA serial numbers are stored in the format recommended by IETF and RIPE, the number of daily changes of the SOA record is limited by 98 times. If you change a SOA record in a domain 98 times during one day, the SOA serial number cannot be changed any more, clicking the Default button will remove all the records from the DNS zone, and the DNS service for the DNS zone cannot be switched on/off or switched to slave/master mode. |